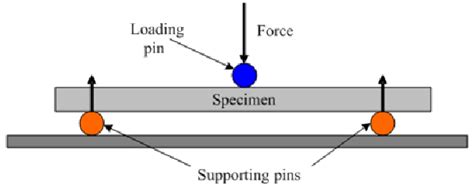
3 point tensile test|3 point bending test dimensions : bulk Due to the three pressure points at the pins, this test arrangement is also called three-point flexural test. In a flexural test, a standardized specimen is bent under uniaxial bending stress until plastic deformation or fracture . The Company is licensed and regulated by the Malta Gamin.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Electronica-pt.com é um site dedicado aos esquemas de elet.
The three-point flexural test measures the flexural properties of materials by applying a load at the midpoint of a supported beam, providing insights into flexural strength, .
The three point bend test (Figure 1) is a classical experiment in mechanics, used to measure the Young’s modulus of a material in the shape of a beam. The beam, of length L, rests on two .The three-point bending technique is a material testing method which evaluates modulus of elasticity in bending, flexural stress and flexural strain when the material sample is set up as a . Due to the three pressure points at the pins, this test arrangement is also called three-point flexural test. In a flexural test, a standardized specimen is bent under uniaxial bending stress until plastic deformation or fracture .The 3-point flexure test to ASTM D790 is a traditional standardized characterization method for rigid and semi-rigid plastics. The flexural properties determined with these tests are of great importance to designers, engineers .
The 3-point bending test bears this name because there are three pressure points in this test setup: Two supports and a centrally loaded test punch. The specimen lies crosswise on the supports and protrudes at the sides. The 3 .present lab session deals with a three-point-bending test to obtain the following material parameter • Stress vs. engineering strain curve and stress vs. real strain curve • Flexural .

three point flexural test
The 3-point and 4-point flexural tests are common methods used to assess the bending properties and strength of materials. Both tests involve applying a load to a test specimen at specific points. Below, we will describe the main types of . Measurement of Load and Displacement. All testing systems have some sort of “loading train”, of which the sample forms a part.This “train” can be relatively complex - for example, it might involve a rotating worm drive . What is a tensile test?In the field of materials science and engineering, a tensile test is a widely used method to determine the mechanical properties of a material, specifically its response to tensile forces. It involves subjecting a specimen to an ever-increasing tensile load until it reaches its breaking point. By measuring the applied force and the resulting .
Also, the 3-point bending test creates tensile failure at one specific point in the cross-section directly under the load application, however, the 4-point bending test subjects several points between load applications to the . Tensile or tension testing is a fundamental and most commonly used test for the characterization of the mechanical behavior of materials. The test consists of pulling a sample of material and measuring the load and the corresponding elongation. . The upper yield point is defined by the tensile standard ISO 6892-1 for metals as follows .When we reach point 3, we can determine the tensile strength or maximum stress (or load) the material can support. It is not a very useful property, since the material has permanently deformed at this point. Ultimate Tensile Stress (UTS) and Ductility. It may be noted at this point that it is common during tensile testing to identify a “strength”, in the form of an “ultimate tensile stress” (UTS).This is usually taken to be the peak on the nominal stress v. nominal strain plot, which corresponds to the onset of necking.
Tensile tests are used to determine how materials behave under tension load. In a simple tensile test, a sample is typically pulled to its breaking point to determine the ultimate tensile strength .
In a 3-point bend test, the convex side of the sheet or plate is placed in tension, and the outer fibers are subjected to maximum stress and strain. Failure will occur when the strain or elongation exceeds the material’s limits. Fracture toughness can be determined using a three-point flexural test. In this case, a pre-notched sample is used .The 3-point and 4-point flexural tests are common methods used to assess the bending properties and strength of materials. Both tests involve applying a load to a test specimen at specific points. . Flexural testing is often correlated with other mechanical tests, such as tensile testing, to provide a comprehensive understanding of a material .Method A is based on the increase in tensile stress during load application. In the linear elastic part of the tensile test, that is at the very beginning of the test, the rate of stress application must be between 1.15 and 11.5 MPa/sec (this corresponds to 10000 and 100000 psi/min).; However, it is clearly stated in ASTM E8 and ASTM E8M that these specifications and method do not .Tensile Test: The main principle of the tensile test is denotes the resistance of a material to a tensile load applied axially to a specimen. It is very important to the tensile test to be considered is the standard dimensions and profiles are adhered to. The typical progress of tensile test can be seen in figure. tensile test done on utm .
In the 3-point bending test, the area offered under the applied load to withstand the stress is less as compared to the area offered in 4- the point load bending test. As a result, the distribution of maximum stress is more uniform and wider in the 4- the point bend test as compared to the 3-point bend test.This test is performed on a universal testing machine (tensile testing machine or tensile tester) with a 3 point or 4 point bend fixture. The key analysis when performing bend testing are: Flexural Modulus – This measures the slope of a stress / strain curve and is an indication of a material’s stiffness;
In a 3-point bending flexural test, a standardized specimen is bent under uniaxial bending stress until plastic deformation or fracture occurs. In this way, . The tensile Testing method measures the force required to break a metallic, composite, or plastic specimen and the extent to which the specimen stretches or elongates to that breaking point. Tensile Test Procedure. A .This test setup includes a 3400 Series test system with a 3-point bend fixture and no extensometer, meaning that strain in this case must be measured by crosshead displacement (Type 1 testing). Whenever strain is measured via .accommodate tensile, compressive, and bending experiments. The data obtained from this test are the load (F) measured by the load cell, the machine displacement (d) and, if a crack-mouth opening . The specimen used for the three-point bending test is a beam similar to the one sketched in Figure 3.
Tensile Testing is a form of tension testing and is a destructive engineering and materials science test whereby controlled tension is applied to a sample until it fully fails. . The yield strength is the point at which plastic deformation occurs under stress. This is determined during testing over a measured gauge length via the use of .
Place the test bar on the 3 point bend fixture and begin the test and end after bending to 5% deflection or until the sample breaks. . Use a standard size test bar if possible! In tensile tests that have samples that are always different sizes all you have to do is enter the width, thickness, and gage length of a sample. However, for D790 .Both the load (stress) and the test piece extension (strain) are measured and from this data an engineering stress/strain curve is constructed, Fig.3.From this curve we can determine: a) the tensile strength, also known as the ultimate tensile strength, the load at failure divided by the original cross sectional area where the ultimate tensile strength (U.T.S.), σ max = P max /A 0, .
Flexural test evaluates the tensile strength of concrete indirectly. It tests the ability of unreinforced concrete beam or slab to withstand failure in bending. . Fig.3: Center Point Load Test (ASTM C293) It should be noticed that, the modulus of rupture value obtained by center point load test arrangement is smaller than three-point load .The tensile strength R m is determined with a tensile test (e.g. in accordance with the ISO 6892 series of standards (for metallic materials), or the ISO 527 series of standards (for plastics and composites)).. The tensile strength is calculated from the maximum achieved tensile force F m and the specimen cross-sectional area at the start of the test: .
The resulting data - a curve of force vs extension - shows the tensile profile of the test up to the point where the specimen breaks. Along this tensile profile there are many points of interest, chief among them the elastic limit and force to break or failure point.
In a simple tensile test, a sample is typically pulled to its breaking point to determine the ultimate tensile strength of the material. The amount of force (F) applied to the sample and the elongation (∆L) of the sample are measured throughout the test. . Tensile testing can also be used to verify that materials adhere to minimum strength .
Examples of destructive tests are tensile tests, bending tests, impact tests, and fatigue tests. Hardness tests are also done on test pieces . ISO 178 is the standard describing the 3-point bending test method for plastic/polymer materials and ASTM D6272 for 4-point bending test of polymers. The samples being tested also have to followThe area up to the yield point is termed the modulus of resilience, and the total area up to fracture is termed the modulus of toughness; these are shown in Figure 13.Tensile Test 3 จากรูปที่ 2 เป นการดึงชิ้นทดสอบอย างช าๆ ชิ้นทดสอบจะค อยๆ ยืดตัวออกจนถึงจุด A ในช วงนี้ . (Yield point) และ .
three point bend test pdf
webSilvanno Salles. 23. Sangue de Gelo. Silvanno Salles. Baixar CD Completo Silvanno Salles - Paredão Apaixonado 2024, Faixas: Dependente, Tô Fazendo Falta, Chorei Na .
3 point tensile test|3 point bending test dimensions